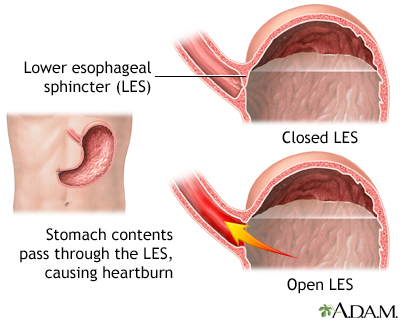
Chronic symptoms or mucosal damage produced by the abnormal reflux in the esophagus
Transient or permanent changes in the barrier between the esophagus and the stomach, may be due to incompetence of the cardia, transient cardia relaxation, impaired expulsion of gastric reflux from the esophagus, or a hiatus hernia.
Symptoms
Heartburn is the major symptom of acid in the esophagus, characterized by burning discomfort behind the breastbone (sternum)
- Esophagitis (reflux esophagitis) — inflammatory changes in the esophageal lining (mucosa)
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Chronic chest pain
- Cough, hoarseness, voice changes, chronic ear ache, nausea
- Sinusitis

H2-receptor Antagonists
- H2-receptor antagonists reduce secretion of gastric acid by blocking H2-receptors.
- Used in short-term treatment of active duodenal ulcers and prevention of ulcer recurrence.
- Also used for heartburn.
Examples of H2 Receptor Antagonist
Pepcid AC, Zantac, Axid
H2-receptor Antagonists: Adverse Effects
Common Adverse Effects: GI disturbances, headache, drowsiness, confusion, agitation, hallucinations, and reversible impotence
Serious Adverse Effects: cardiac arrhythmias and cardiac arrest after IV bolus dose
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Act by blocking hydrochloric acid production
Used to heal stomach and duodenal ulcers and relieve symptoms of GERD and esophagitis
Examples
Prevacid
No comments:
Post a Comment